Objectives
Upon completion of this chapter, you will be able to answer the following questions:
- What are common network applications?
- How does DNS operate?
- How do HTTP and HTML operate?
- How does FTP operate?
- How do Telnet and SSH operate?
- How do email protocols operate?
Key Terms
This chapter uses the following key terms. You can find the definitions in the Glossary.
Domain Name System (DNS) page 231
File Transfer Protocol (FTP) page 235
Hypertext Markup Language (HTML) page 233
Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) page 233
Internet Message Access Protocol (IMAP) page 241
Post Office Protocol (POP) page 241
Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP) page 240
Introduction (12.0.1)
What was the first thing you remember doing on the Internet? Did you go to a web page? Send an email? Receive a file? All of these tasks (and others) are possible because of application layer services. There is a lot for a network administrator to know about application layer services, and this is the chapter to introduce you to all of it.
Network Application Services (12.1)
Network application services allow users to use domain names instead of IP addresses, receive information from web servers, access email, and perform file transfers. These are the services in which users interact with networks and the Internet.
Common Network Application Services (12.1.1)
What are the most common Internet services that you use on a regular basis? For most people, the list includes services such as Internet searches, social media sites, video and audio streaming, online shopping sites, email, and messaging. Each of these services relies on protocols from the TCP/IP protocol suite to reliably communicate the information between the clients and servers.
Some of the most common servers that provide these services are shown in Figure 12-1. A brief description of each service is shown in Table 12-1.
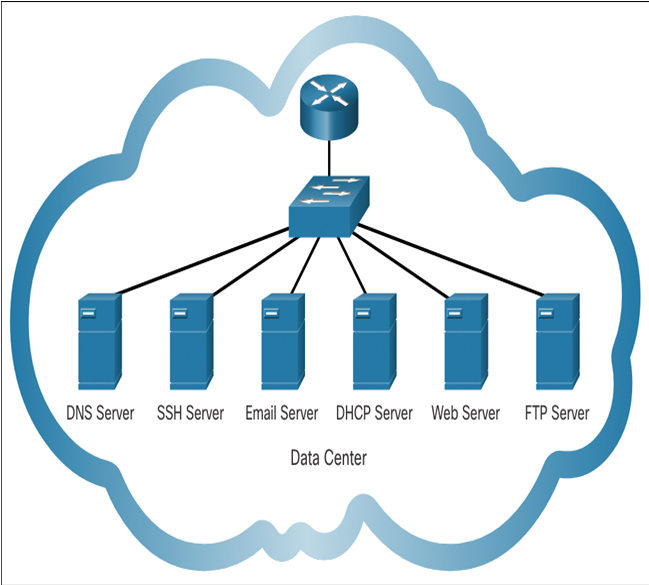
Figure 12-1 Services in a Data Center
Table 12-1 Common Server Protocols
| Protocol | Description |
| Domain Name System (DNS) | Resolves Internet names to IP addresses. |
| Secure Shell (SSH) | Provides remote access to servers and networking devices. |
| Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP) | Sends email messages and attachments from clients to servers and from servers to other email servers. |
| Post Office Protocol (POP) | Used by email clients to retrieve email and attachments from a remote server. |
| Internet Message Access Protocol (IMAP) | Used by email clients to retrieve email and attachments from a remote server. |
| Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) | Used to automatically configure devices with IP addressing and other necessary information to enable them to communicate on a network. |
| Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) | Used by web browsers to request web pages and by web servers to transfer the files that make up web pages. |
| File Transfer Protocol (FTP) | Used for interactive file transfer between systems. |

